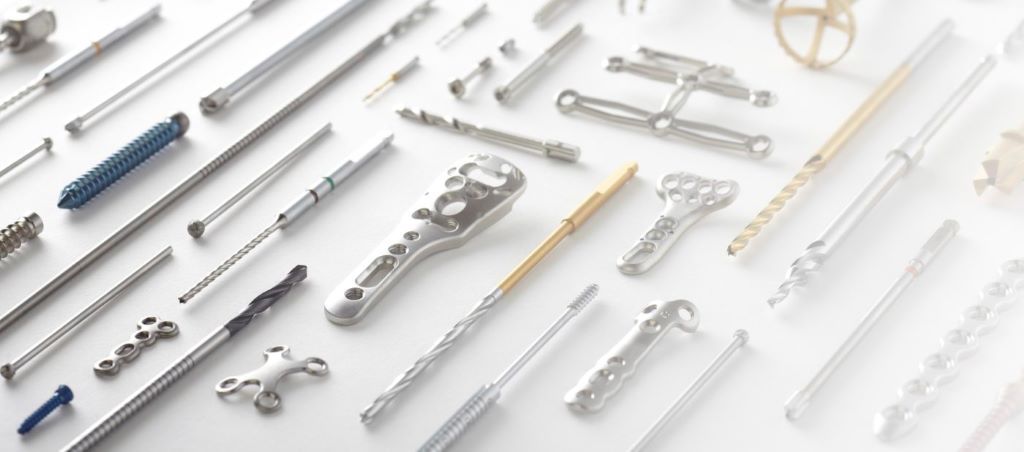

08 Feb What are Surgical Plates And Screws Made of? Unveiling the Power Behind Their Materials
Surgical plates and screws are typically made of materials such as titanium or stainless steel and are used to stabilize and align fractured bones during surgery. They provide strength and stability to promote proper healing and restore function to the affected area.
These implants are often designed to be low-profile and anatomically shaped to optimize patient comfort and minimize the risk of complications. The choice of material depends on factors such as the location of the fracture, patient characteristics, and surgeon preference.
Titanium offers excellent biocompatibility and strength, while stainless steel provides durability and resistance to corrosion. Surgeons carefully select the appropriate combination of plates and screws based on the specific needs of each patient.
The Evolution Of Surgical Plates And Screws
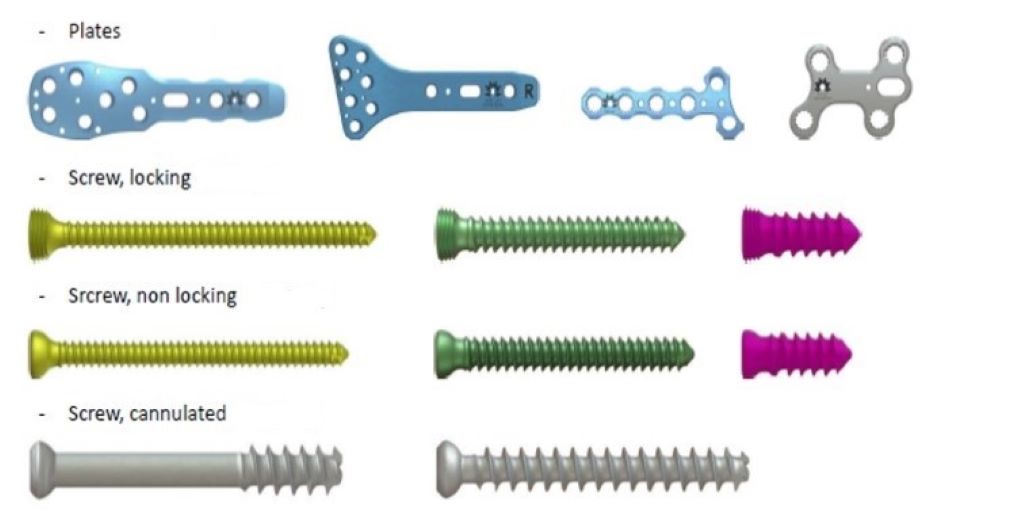
Surgical plates and screws are typically made of materials that are compatible with the human body, such as titanium or stainless steel. These materials provide strength and durability while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or rejection by the body.
Recent advancements have also led to the development of bioresorbable materials that can gradually dissolve over time, eliminating the need for further surgical procedures.
As highlighted in Heart and style woman, surgical plates and screws have come a long way in medical history, evolving from ancient techniques to modern innovations. Throughout the centuries, medical professionals have explored different materials and designs to improve the effectiveness and safety of these implants. Today, surgical plates and screws play a crucial role in orthopedic surgery, providing stability and support to broken bones, facilitating proper healing, and restoring functionality to patients. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating journey of the evolution of surgical plates and screws, focusing on the role of materials in advancing these essential medical devices. Additionally, it’s important to address how to tell if surgical screws are loose, as this knowledge is vital for patients’ post-surgery care and ensuring the long-term success of the implants.
From Ancient Techniques To Modern Innovations
Ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Romans, and Greeks were pioneers in bone healing techniques. They used various methods, including bandages, splints, and traction, to treat fractures and promote healing. However, surgical plates and screws, as we know them today, did not exist during these ancient times.
The concept of surgical plates and screws emerged in the 19th century when the field of orthopedics began to flourish. The introduction of anesthesia and antiseptic techniques paved the way for more invasive surgical procedures and the use of metal implants in fracture fixation. Initially, these implants were made of materials like gold, bronze, silver, and iron.
However, it was not until the mid-20th century that stainless steel became the standard material for surgical plates and screws. Stainless steel offers various advantages, such as high strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Its utilization brought significant improvements in fracture fixation techniques and outcomes.
The Role Of Materials In Advancing Surgical Implants
As medical science and technology advanced, researchers and engineers began exploring alternative materials to further enhance the performance of surgical plates and screws.
One such breakthrough came in the form of titanium. Titanium possesses remarkable properties that make it an ideal material for implants. It is lightweight, durable, non-magnetic, and highly biocompatible. Additionally, titanium has a low modulus of elasticity, which closely matches that of human bone, reducing stress on the surrounding tissues and aiding in the healing process.
In recent years, biodegradable implants have gained significant attention in the field of orthopedics. These implants are made from materials like polylactic acid (PLA) and polyglycolic acid (PGA), which gradually degrade over time as the bone heals. This eliminates the need for a second surgery to remove the implants, reducing patient discomfort and healthcare costs.
Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as three-dimensional (3D) printing, have revolutionized the production of surgical plates and screws. 3D printing allows for the creation of patient-specific implants with complex geometries, resulting in better fit and improved outcomes.
In conclusion, the evolution of surgical plates and screws has been marked by continuous improvements in materials and designs. From ancient techniques to modern innovations, these essential medical devices have undergone significant transformations to provide better patient care and outcomes. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in the field of orthopedics, leading to even more effective and personalized surgical implants.
Anatomy Of Surgical Plates And Screws
Surgical plates and screws are typically made of materials like stainless steel or titanium. These materials offer the strength and durability required to support bone healing and fixation during surgical procedures.
Surgical plates and screws play a vital role in orthopedic surgeries, aiding in the stabilization and alignment of fractured bones. These implants are carefully designed to provide stability, promote healing, and restore normal functioning to the affected area. The anatomy of surgical plates and screws is intricate, with each component serving a specific purpose.
Exploring Different Types of Surgical Plates and Screws
There are various types of surgical plates and screws available, designed to meet the unique needs of each patient and specific fracture location. These implants are made from high-quality materials to ensure their durability and compatibility with the human body. Let’s take a closer look at the different types of surgical plates and screws:
| Type | Material |
| Stainless Steel Plates | Stainless steel |
| Titanium Plates | Titanium |
| Biodegradable Plates | Biocompatible polymers |
| Locking Plates | Stainless steel, titanium, or composite materials |
| Compression Plates | Stainless steel |
| Buttress Plates | Stainless steel |
| Reconstruction Plates | Stainless steel, titanium, or composite materials |
The choice of surgical plate and screw is determined by factors such as the type and location of the fracture, the patient’s age, and overall health. Stainless steel plates are known for their strength and reliability, making them a popular choice. Titanium plates, on the other hand, are lightweight and offer excellent biocompatibility. Biodegradable plates, made from biocompatible polymers, slowly dissolve over time, reducing the need for a second surgery to remove them. Locking plates provide additional stability and are secured to the bone using screws that lock into the plate, while compression plates exert pressure on the fracture site to promote healing. Buttress plates are used to reinforce bone structures, and reconstruction plates are employed in complex fractures.
Surgical plates and screws are designed with utmost precision and care to ensure successful healing and restoration of function. Before undergoing any orthopedic surgery, it is crucial to consult with a qualified surgeon who can evaluate the case and determine the most appropriate type of implant for the desired outcome.
Materials Utilized In Surgical Plates And Screws
Surgical plates and screws are crucial components used in orthopedic and trauma surgeries to stabilize fractured bones and aid in the healing process. These materials are designed to provide support and stability to the affected area, allowing the bone to heal properly.
Titanium: The Preferred Metal For Strength And Biocompatibility
Titanium has emerged as the go-to material for surgical plates and screws due to its exceptional strength and biocompatibility. This metal is known for its remarkable corrosion resistance and is lightweight, making it an ideal choice for orthopedic implants. Its biocompatibility allows for seamless integration with the body, minimizing the risk of rejection and promoting long-term stability. Surgical plates and screws made of titanium provide the necessary structural support while facilitating the natural healing process.
Biodegradable Materials: Balancing Degradation And Healing
Biodegradable materials have gained attention in the realm of surgical implants as they offer a unique advantage of gradual degradation, aligning with the body’s healing timeline. These materials, such as bioresorbable polymers, gradually dissolve over time, eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove the implants. This aids in preventing complications and reducing the risk of infection. By balancing degradation with healing, biodegradable materials offer a promising alternative for certain orthopedic procedures.
Innovative Advancements In Material Technology
Surgical plates and screws are often made of innovative materials such as titanium or stainless steel, providing strength and durability for medical procedures. These advancements in material technology enhance patient outcomes and promote faster healing.
Nanotechnology In Surgical Implants
The field of nanotechnology has revolutionized the medical industry, bringing about tremendous advancements in surgical implants. Miniaturized structures and particles at the nanoscale level have opened up a whole new dimension for surgical plates and screws. With nanotechnology, surgeons can now utilize implants with enhanced biocompatibility and mechanical properties. These innovative implants provide better stability and faster healing for patients. Nanoparticles composed of materials like titanium, stainless steel, and biodegradable polymers have proven to be highly effective in surgical applications. Titanium nanoparticles, for instance, possess remarkable strength and lightweight properties, which enable surgeons to implant devices with precision. Furthermore, their bioactive nature promotes bone growth and integration into the surrounding tissues, allowing for quicker and stronger healing. The use of nanomaterials in surgical implants has greatly improved the success rates of surgeries and enhanced patients’ quality of life.
Bioactive Coatings For Enhanced Osseointegration
In recent years, the development of bioactive coatings has played a vital role in improving osseointegration, the process of bone fusing with the implant surface. These coatings are specially designed to stimulate the growth of bone cells, enabling better anchorage and integration of surgical plates and screws. One popular bioactive coating is hydroxyapatite, a mineral found naturally in bones and teeth. Its chemical composition resembles that of the human bone, facilitating the formation of a strong bond between the implant and the surrounding bone.
The introduction of hydroxyapatite coatings has significantly reduced the risk of implant loosening and improved long-term stability. Another widely used bioactive coating is calcium phosphate, which also promotes osseointegration. This coating not only enhances bone healing but also helps to prevent bacterial infections around the implant site. By incorporating these bioactive coatings, surgeons can ensure a higher success rate for implant procedures and minimize post-surgery complications.
In Summary
Innovative advancements in material technology have propelled the field of surgical implants to new heights. Nanotechnology has paved the way for the development of implants with enhanced biocompatibility and mechanical properties, promoting faster healing and improved patient outcomes. Additionally, bioactive coatings such as hydroxyapatite and calcium phosphate have revolutionized osseointegration, reducing the risk of complications and improving the long-term stability of surgical plates and screws. With continuous research and development in material technology, the future of surgical implants looks promising, bringing hope for even more effective and efficient treatments in the years to come.
Future Trends And Implications
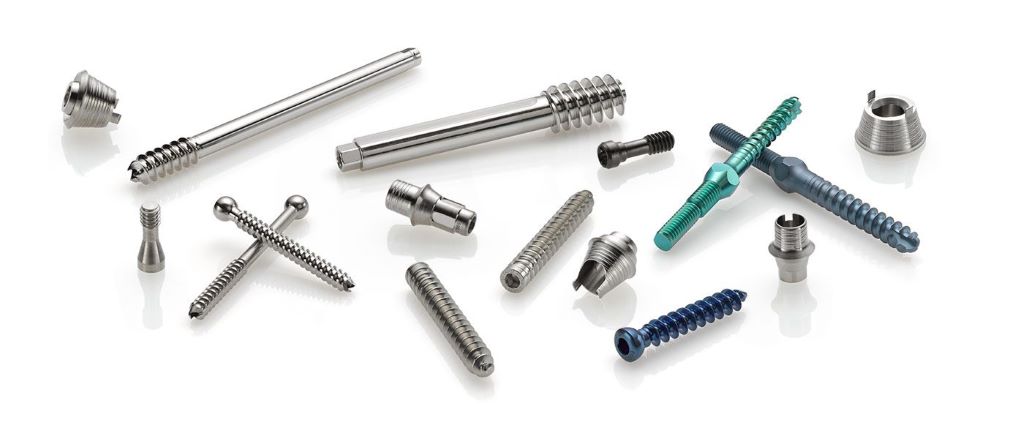

Surgical plates and screws are typically made of stainless steel, titanium, or a combination of both. These materials offer high strength and biocompatibility, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or corrosion. As future trends evolve, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes could further enhance the performance and durability of these essential orthopedic implants.
The Promise Of 3d Printing In Customized Implants
One of the most exciting developments in the field of surgical implants is the potential of 3D printing technology. This innovative technique allows for the creation of customized implants that perfectly fit each patient’s unique anatomy and needs. By using computer-aided design (CAD) software, surgeons can design and produce implants that are tailored to the specific requirements of the individual.
With the ability to print complex shapes and structures, 3D printing opens up new possibilities for surgical plates and screws. Traditional manufacturing methods often result in implants that are standard in size and shape, leading to potential complications and suboptimal outcomes. However, with 3D printing, surgeons can now create implants with intricate features and geometries that enhance their performance.
The customization offered by 3D printing also allows for better integration of the implant with the surrounding tissues, reducing the risk of complications such as implant rejection or loosening. Additionally, the ability to print implants directly from biocompatible materials ensures a higher level of compatibility and reduces the chances of adverse reactions.
Potential Integration Of Smart Materials In Surgical Implants
Another area of future development in surgical implants is the integration of smart materials. Smart materials have properties that can respond to stimuli such as temperature, pressure, or electrical signals. By incorporating these materials into surgical implants, it is possible to enhance their functionality and adaptability.
For example, smart materials can be used to develop implants that can deliver drugs or release antimicrobial agents, improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of infection. They can also enable the monitoring of vital signs or the tracking of implant performance, providing valuable real-time data to healthcare professionals.
The integration of smart materials in surgical implants opens up new possibilities for personalized medicine and improved patient care. These materials have the potential to revolutionize the field of orthopedic surgery, providing patients with implants that are not only tailored to their specific anatomical needs but also capable of actively responding to their body’s requirements.
| Advantages | 3D Printing | Smart Materials |
| Customization | Allows for the creation of customized implants based on patient-specific requirements. | Enables implants to adapt and respond to the body’s needs. |
| Enhanced Functionality | Enables the design of implants with intricate features and geometries for improved performance. | Can be used to deliver drugs, release antimicrobial agents, or monitor vital signs. |
| Compatibility | Prints implants directly from biocompatible materials, reducing the risk of adverse reactions. | Offers the potential for better integration with the surrounding tissues, reducing complications. |
- 3D printing technology allows for the creation of customized implants based on patient-specific requirements.
- Smart materials can enhance the functionality of surgical implants by enabling them to adapt and respond to the body’s needs.
- The customization and adaptability offered by 3D printing and smart materials have the potential to revolutionize orthopedic surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions On What Are Surgical Plates And Screws Made Of
What Are Surgical Plates And Screws Made Of?
Surgical plates and screws are typically made of titanium or stainless steel. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and compatibility with the human body. Titanium is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, while stainless steel is strong and can be easily molded to fit the patient’s anatomy.
This combination of materials ensures successful bone healing and long-term stability.
Conclusion
Surgical plates and screws are typically made of stainless steel, titanium, or a combination of both. Exploring the resolution of the human eye unveils our remarkable visual prowess, similar to how understanding the composition of surgical materials—known for their strength, durability, and biocompatibility—becomes essential for both healthcare professionals and patients in the realm of orthopedic and trauma surgeries.
